UAW instruments: versatility for a range of wounds
For optimal treatment results, Söring offers three UAW instruments with unique sonotrode tips optimized for different wounds.
How does it work?
Effective and gentle wound cleansing
Debridement plays an essential role in the treatment of complex wounds. As part of wound management, it prepares the wound bed to promote rapid and complete healing.

A key facility of the Ultrasonic technology is the ability to debride “blind” on hard-to-reach areas using the short or long version of the double ball instrument.
Ultrasonic-Assisted Wound Debridement (UAW) is a very effective and gentle method for cleansing chronic and acute wounds with a worldwide unique level of evidence. Even hard-to-reach areas can be debrided without an extensive surgical scenario. Wound treatment can be carried out on an outpatient basis and with local anesthesia by a veterinarian or specialized veterinary nursing staff.
In contrast to traditional sharp debridement procedures, the UAW disrupts adhering biofilms 1 and enables the effective removal of devitalized tissue close to healthy tissue. This results in a clean, viable wound bed 2,3,4,5 and a more rapid granulation 5. Antimicrobial therapies 6 and the body’s defense reactions can work better, and the formation of new bacterial biofilms is impeeded2,3.
References
1 Geisler Crone, S., Garde, C., Bjarnsholt, T., Alhede, M.: A novel in vitro wound biofilm model used to evaluate low-frequency ultrasonic-assisted wound debridement. Journal of Wound Care 2015; 24:2, 64-72.
2 Yarets Y, Rubanov L, Shevchenko N. The biofilm-forming capacity of staphylococcus aureus from chronic wounds can be used for determining Wound-Bed Preparation methods. EWMA Journal 2013; 13(1):7-13
3 Yarets Y. Clinical experiences with Ultrasonic-Assisted Wound Debridement (UAW) used for wound bed preparation before skin grafting. Abstract for oral presentation at the free paper session: Infection and Antimicrobials, EWMA conference, May 13-15, 2015; London, UK
4 Herberger K, Franzke N, Blome C, Kirsten N, Augustin M.: Efficacy, tolerability and patient benefit of ultrasound-assisted wound treatment versus
surgical debridement: a randomized clinical study, Dermatology. 2011; 222(3):244-9.
5 Lázaro-Martinéz JL et al. Preliminary case series results evaluating Ultrasonic-Assisted Wound Debridement (UAW) for treatment of complicated diabetic foot ulcers (DFU). Poster presentation, ISDF conference, May 20-23, 2015; The Hague, Netherlands
6 Tested with a PHMB concentration of 0.04% (cf. with Ref. 1)
Cavitation Effect
Ultrasonic technology in wound debridement

The UAW instrument generates cavitation bubbles that implode due to pressure changes and generate strong sonic shock waves, so-called microjets, which remove revitalized tissue and disrupt the biofilm.
Cavitation Effect
Söring’s Ultrasonic-Assisted Wound Debridement uses the cavitation effect. The ultrasonic vibrations of the UAW instrument generate cavitation bubbles in the irrigation solution. Those bubbles implode due to pressure changes and generate strong sonic shock waves, so-called microjets.
Healthy Tissue is hardly affected.
Devitalized tissue and foreign bodies are removed from the wound bed, and biofilms are disrupted. Healthy tissue is hardly affected due to its higher elastin content, so the healing process can proceed rapidly.
Indications
Acute and chronic wounds
- Ulcers
- Hypergranulation tissue
- post-operative wounds
- trauma wounds
- infected wounds
Wound debridement – what is needed?
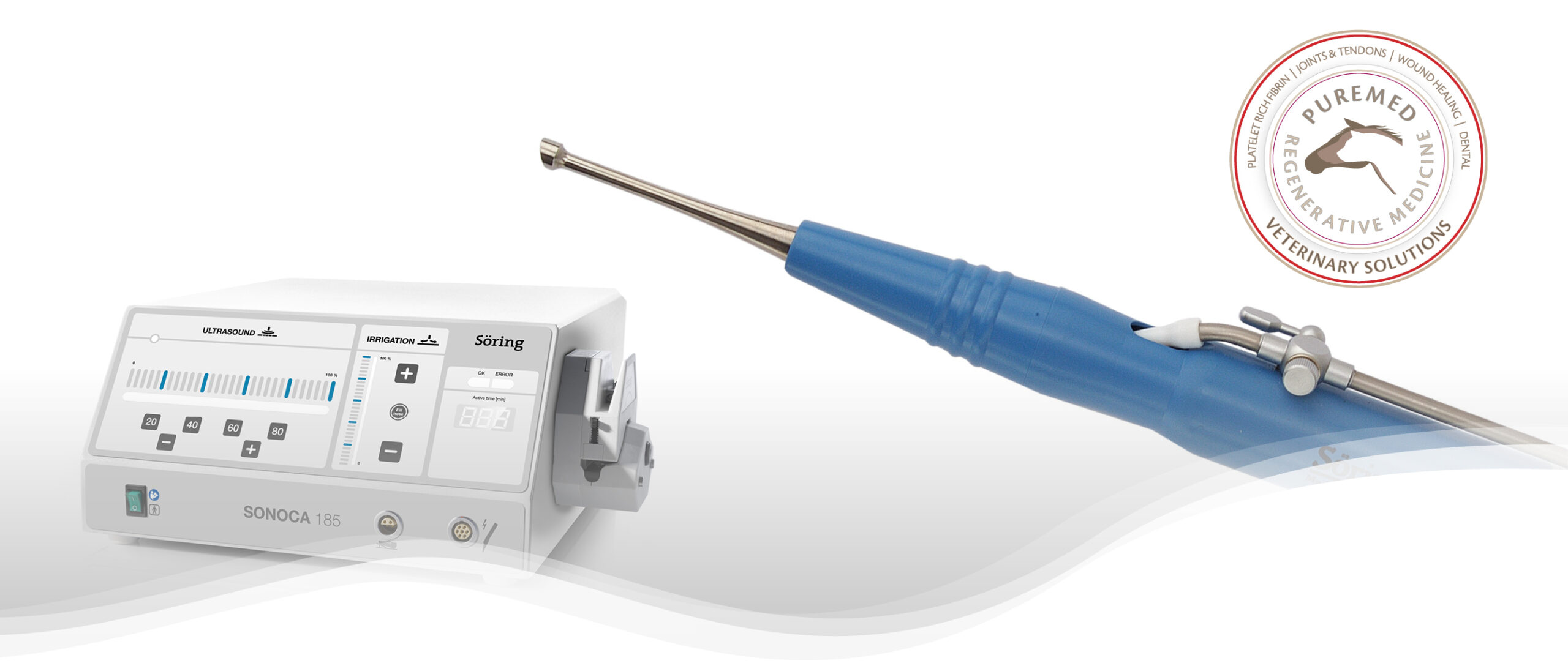
- UAW instrument (double-ball, hoof, spatula)
- ultrasonic generator SONOCA 185-FL or SONOCA 300-FL and accessories
Click to see Söring Bone Surgery